Updated on July 08, 2025 12:03:55 PM
A barcode is “A machine-readable code in the form of numbers and a pattern of parallel lines of varying widths, printed on and identifying a product.”
The lines and patterns on a barcode are actually representations of numbers and data and their development allowed basic information about a product to be easily read by an optical scanning device (a barcode scanner) and automatically entered into a computer system. This massively reduces the time to record products information and eliminates human data entry error.
Barcode systems help businesses and organizations track products, prices, and stock levels for centralised management in a computer software system allowing for incredible increases in productivity and efficiency.
Barcodes started out with simple 1-dimensional designs, consisting of basic black lines that could only be read by specially designed barcode scanners. However, today barcodes come in many shapes and sizes and a wide range of designs and many can even be read by mobile phones and other devices.
.jpeg)
Provides unambiguous & universal identification of products so no two products in the world would have the same GS1 barcode number.
Helps with faster listing of products on e-commerce platforms.
Meets pre-requisite to doing business with modern trade retailers.
Gives an international look and feel to products..
Facilitates accurate and faster billing at retail billing counters.
Since the barcode is a unique key to identify a product (via GTIN), it can be used to identify products without any ambiguity and place accurate orders for them.
With Product Barcodes, company can use the technology to maintain accurate control over inventory. For example, warehouses and retailers can scan barcodes when products arrive and leave, to take a record of inventory. Some companies link their inventory control to online portals so that they can instantly update package status.
Enables automated data capture with 100% information accuracy. This helps eliminate human errors, offering a reliable way to read encoded information.
Different application requires different barcodes with capability to hold different data. Therefore, to diverse requirements, Barcode system standards are used for that distinction between barcodes. Different types of barcode symbols are also distinction between different barcodes. Barcodes can be categorized into the following categories:
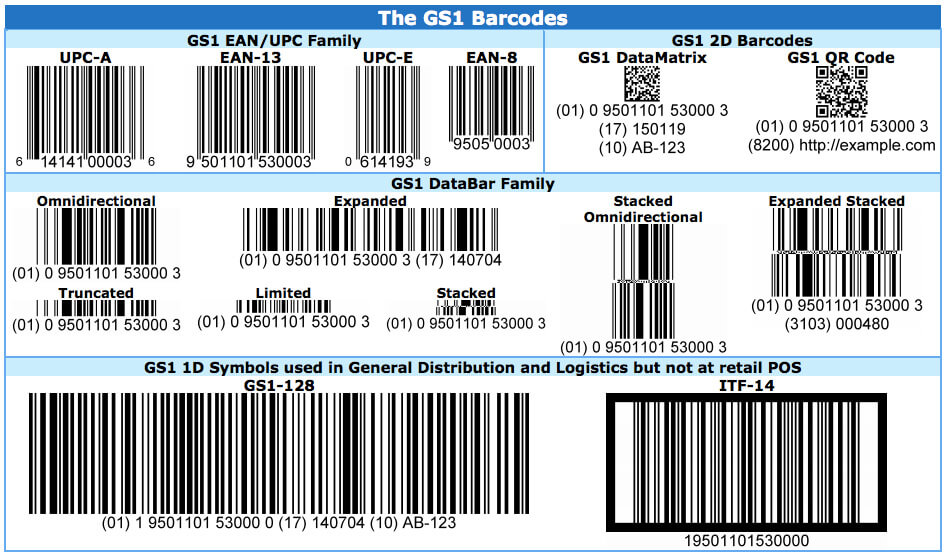
EAN/UPC (European Article Number/Uniform Product Code) Family of barcodes is instantly-recognizable barcodes that are printed on virtually every consumer product in the world. They are the longest-established and most widely-used of all barcodes. Used for Retail stores for sales checkout; inventory, etc.
DataBar barcodes are often used to label fresh foods. These barcodes can hold information like an item’s batch number or expiry date, in addition to other attributes used at the point-of-sale such the item weight.
128 and ITF-14 are highly versatile 1D barcodes that enable items to be tracked through global supply chains. The 128 barcode can carry any of the ID keys, plus information like serial numbers, expiration dates and more. The ITF-14 barcode can only hold the Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) and is suitable for printing on corrugated materials.
Two-dimensional (2D) barcodes look like squares or rectangles that contain many small, individual dots. A single 2D barcode can hold a significant amount of information and may remain legible even when printed at a small size or etched onto a product. 2D barcode could do much more than just keep track of assets and inventory.
Today, 2D codes, especially QR codes, which can hold as much as 7,000 digits or 4,000 characters of text, are used by companies to share information or websites and videos with consumers, or by healthcare facilities to monitor medication, and even to integrate data with programs like MS Office, MS SQL Servers, and other databases and files.
2D barcodes are used in a wide range of industries, from manufacturing and warehousing to logistics and healthcare.
Barcodes work through the combination of a symbology (the barcode) and a scanner that can read the symbols and convert them into useful information, often information about an item’s origin, price, type, and location. The scanner reads the barcode and automatically enters the information stored in it into a system – often some type of database.
This tool has provided many, many benefits for businesses. It paved the way for the globally connected distribution channels we now have and it is what allows big Departmental Stores like BigBazaar, Walmart, Pentaloon to ensure they have products properly stocked and priced around the stores located in all cities. It has also become a crucial tool to help small and medium businesses, as well as hospitals and government groups, keep track of assets and improve their efficiencies.
Some of the ways businesses use barcodes include:
Provided all barcodes registration taken at a time
Provided all barcodes registration taken at a time
Provided all barcodes registration taken at a time
First, Get Consultation from our Consultant to know the Documents Requirements, Registration Cost, Subscription, Barcodes type, Numbers of Barcodes and process of registration.
Once your documents reached to us, We prepare your application along with the “Product Sheet". you can take more than one barcode in one application subject to maximum limit as per option availed by you. Maximum Barcode limit is 100000.
Once your application is completed in all respect, we proceed to file your application with GS1 India and Pay Fees.
.jpeg)
We Track the application status and update Client time to time.
GS1 India, Issue Certificate for all Barcodes.
At Professional Utilities, we leverage our industry knowledge and expertise to help businesses navigate complex regulations, minimize risks, and optimize operations for maximum efficiency and profitability.






"Explore how Professional Utilities have helped businesses reach new heights as their trusted partner."

It was a great experience working with Professional Utilities. They have provided the smoothly. It shows the amount of confidence they are having in their field of work.

Atish Singh
It was professional and friendly experience quick response and remarkable assistance. I loved PU service for section 8 company registration for our Vidyadhare Foundation.

Ravi Kumar
I needed a material safety data sheet for my product and they got it delivered in just 3 days. I am very happy with their professional and timely service. Trust me you can count on them.

Ananya Sharma
Great & helpful support by everyone. I got response & support whenever I called to your system. Heartly thanx for Great & Super Service. Have a Great & Bright future of team & your company.

Prashant Agawekar
Thank you so much Professional Utilities team for their wonderful help. I really appreciate your efforts in getting start business. Pvt Ltd company registration was smooth yet quick.

Abhishek Kumar
I applied for Drug licence and company registration and their follow-up for work and regular updates helped me a lot. They are happily available for any kind of business consultancy.

Vidushi Saini
Great experience went to get my ITR done, process was quite convenient and fast. Had a few queries, am happy about the fact those people explained me all things I wanted to know.

Taniya Garyali
Great services provided by Professional Utilities. They are best in this industry and the best part is their prices are so affordable. Kudos to you. Now you guys are my full-time consultant.

Aftab Alam